A) (Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment ÷ Percent of a brand's total U.S. sales in a market segment) × 100
B) (Percent of a product category's total U.S. sales in a market segment ÷ Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment) × 100
C) (Percent of a brand's total U.S. sales in a market segment ÷ Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment) × 100
D) (Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment ÷ Percent of a product category's total U.S. sales in a market segment) × 100
E) The ratio of sales revenue of the firm to the total sales revenue of all firms in the industry, including the firm itself
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a product in the decline stage of the product life cycle?
A) analog TVs
B) smartphones
C) 3D HDTVs
D) soft drinks
E) tablet devices
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Egg Farmers of Canada implemented its "Get Cracking" advertising campaign, the organization was trying to stimulate __________ demand.
A) secondary
B) selective
C) derived
D) generic
E) primary
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the decline stage of the product life cycle is most accurate?
A) Ironically, in the decline stage, sales decline even though profits increase.
B) A product enters the decline stage only as the result of a major product flaw or marketing misstep.
C) A major reason that a firm's product enters the decline stage is as a result of a change in the marketing environment.
D) The only real step that can be taken to avoid the decline stage and ultimately extinction is to increase marketing expenditures as soon as the product enters its maturity stage.
E) Service industries are exempt from the decline stage because of their intangible natur
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm's marketing dashboard displays a BDI over 100 for a consumer packaged good, such as General Mills' Warm Delights Minis, this indicates which of the following?
A) a weak brand position in a segment
B) a strong brand position in a segment
C) above-average product category purchases by a market segment
D) below-average product category purchases by a market segment
E) There is not enough information to make any conclusions.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At which stage in the product life cycle do industry profits usually peak?
A) introduction
B) growth
C) maturity
D) decline
E) accelerated development
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gatorade Thirst Quencher displays the letter G front and center along with the brand's iconic bolt. According to the company, "G represents the heart, hustle, and soul of athleticism and will become a badge of pride for anyone who sweats, no matter where they're active." This is an example of __________ benefits of its packaging.
A) perceptual
B) functional
C) communications
D) physical
E) tangible
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm's marketing dashboard displays a CDI under 100 for a consumer packaged good, such as General Mills' Warm Delights Minis, this indicates which of the following?
A) a weak brand position in a segment
B) a strong brand position in a segment
C) above-average product category purchases by a market segment
D) below-average product category purchases by a market segment
E) There is not enough information to make any conclusions.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding labels is most accurate?
A) Although labels are can carry useful information, the less information communicated, the better.
B) The brand logo or brand name should always be the largest image on a label.
C) Labels can be very expensive, but they are important because they often are the first contact the consumer has with the product.
D) The best labels to use on food products are those that can be easily removed to promote recycling of the package.
E) One penny for every dollar consumers spend on products goes towards packaging and labeling costs.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
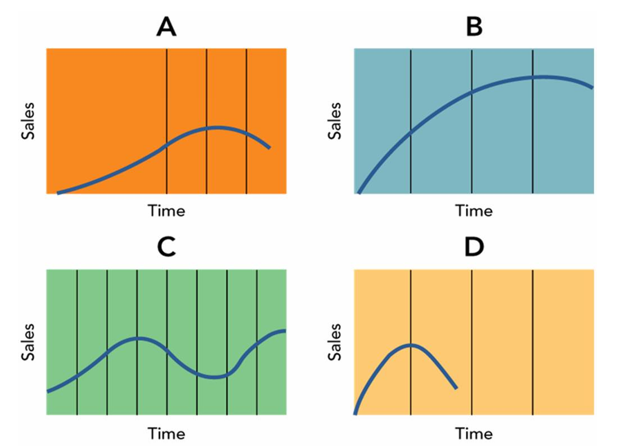 -The product life cycle shown in D in Figure 10-3 above is an example of a __________ product.
-The product life cycle shown in D in Figure 10-3 above is an example of a __________ product.
A) high-learning
B) low-learning
C) fashion
D) fad
E) generalized
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
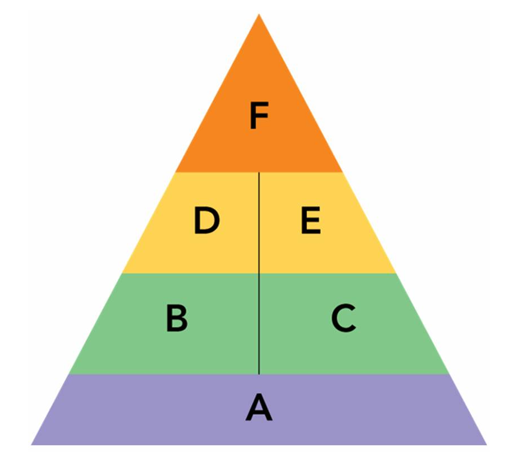 -Figure 10-5 above shows the sequential process of building brand equity. Segment A represents the first step, which is to __________.
-Figure 10-5 above shows the sequential process of building brand equity. Segment A represents the first step, which is to __________.
A) create a consumer-brand connection
B) develop positive brand awareness
C) reward loyal customer behavior
D) establish a brand's meaning in the minds of consumers
E) elicit the proper consumer responses to a brand's identity and meaning
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
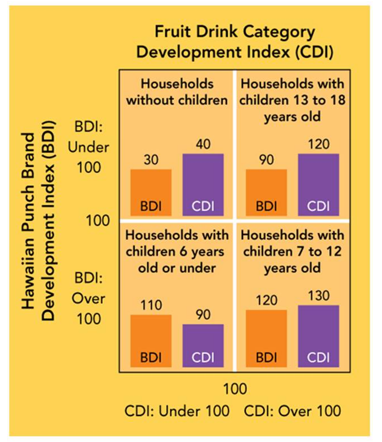 -As shown in the CDI/BDI Marketing Dashboard above, a BDI of 30 is determined by __________.
-As shown in the CDI/BDI Marketing Dashboard above, a BDI of 30 is determined by __________.
A) finding the percent of the U.S. population in the "Households without children" segment divided by the percent of Hawaiian Punch sold to households without children in the U.S. multiplied by 100
B) subtracting the total number of non-users from the total number of users of Hawaiian Punch sold to households without children
C) finding the difference in total sales of Hawaiian Punch between households who have children with those who do not
D) finding the percent of Hawaiian Punch sold to U.S. households without children divided by the percent of the U.S. population in the "Households without children" segment multiplied by 100
E) using the ratio of sales revenue of the firm to the total sales revenue of all firms in the industry, including the firm itself
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formula to calculate a BDI = __________.
A) (Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment ÷ Percent of a brand's total U.S. sales in a market segment) × 100
B) (Percent of a product category's total U.S. sales in a market segment ÷ Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment) × 100
C) (Percent of a brand's total U.S. sales in a market segment ÷ Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment) × 100
D) (Percent of the total U.S. population in a market segment ÷ Percent of a product category's total U.S. sales in a market segment) × 100
E) The ratio of sales revenue of the firm to the total sales revenue of all firms in the industry, including the firm itself
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A marketing strategy that alters a product's characteristic, such as its quality, performance, or appearance, to increase its value and sales to customers is referred to as __________.
A) market modification
B) product modification
C) product repositioning
D) market-product synergy
E) product management
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
IKEA sells a portable workbench called the FAHRTFULL. The product has many positive features, and in German or Swedish markets, the name describes the product's features well (fahrt meaning travel) . This brand name in the United States, however, may not be as effective due to __________.
A) disappointment when the product fails to perform as the brand name implies
B) the poor attempt at humor, which makes consumers question product quality
C) governmental restrictions on brand names that read or sound like bodily functions
D) its unfavorable phonetic and semantic associations in English
E) difficulty in showing "fahrtfull" in German and Swedish advertising
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A concept that describes the stages a product goes through in the marketplace - introduction, growth, maturity, and decline - is referred to as the __________.
A) retail life cycle
B) product life cycle
C) marketing mix
D) product growth cycle
E) diffusion of product innovation
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brand equity provides a financial advantage for a brand's owner because successful, established brand names have an economic value in the sense that they are __________.
A) tangible assets
B) intangible assets
C) durable goods
D) nondurable goods
E) intangible equity
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alka-Seltzer was originally made as a hangover remedy that cured a headache and settled the stomach. Today, you can purchase Original Alka-Seltzer, Extra Strength Alka-Seltzer, Alka-Seltzer Morning Relief (for morning headaches and fatigue) , and Alka-Seltzer Heartburn Relief, each of which has slightly different ingredients to solve the problem identified in its respective brand name. To broaden the product line to increase sales to new target market segments, the makers of Alka-Seltzer used a __________ strategy.
A) product modification
B) market-product grid
C) diversification
D) market modification
E) product class extension
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacity management refers to
A) integrating the service component of the marketing mix with efforts to influence consumer demand.
B) when the service provider is available but there is no demand.
C) charging different prices during different times of the day or during different days of the week to reflect variations in demand for the service.
D) the practice of changing prices for services in real time in response to supply and demand conditions.
E) the operating cost per hour per employee or technology subtracted from the revenue generated by each full-time employee equivalent.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three main benefits packaging provides to manufacturers, retailers, and consumers are communication benefits, perceptual benefits, and __________ benefits.
A) personal
B) functional
C) financial
D) societal
E) aesthetic
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 408
Related Exams