A) testosterone.
B) nutrients to sustain the sperm.
C) enzymes to allow penetration into the oocyte.
D) mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
E) buffers to neutralize the acidity of the female reproductive tract.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stages that appear during spermatogenesis are A: Spermatid B: Primary spermatocyte C: Spermatogonium D: Spermatozoon E: Secondary spermatocyte What is the correct order of appearance of these stages?
A) b,e,c,d,a
B) c,e,d,a,b
C) c,b,e,a,d
D) a,c,b,e,d
E) d,b,c,e,a
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Menarche is
A) the first four days of menstruation.
B) a female's first menstrual cycle.
C) the stage immediately preceding menopause.
D) marked by a dramatic decline in androgen secretion.
E) the final phase of the uterine cycle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a uterine function?
A) Protection and support of developing embryo
B) Usual site of fertilization
C) Site of implantation
D) Muscle contraction for labor and delivery
E) Passageway for sperm
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these structures contains sebaceous glands?
A) Clitoris
B) Vestibular bulb
C) Mons pubis
D) Labia minora
E) Prepuce
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Developing sperm cells are protected by a blood-testis barrier formed by
A) connective tissue septa.
B) interstitial spaces.
C) Leydig cells.
D) sustentacular cells.
E) leukocytes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fimbriae
A) are extensions of the ovarian ligament.
B) line the ampulla of the uterine tube.
C) enclose the ovary at the time of ovulation.
D) are sloughed off during menstruation.
E) assist in the movement of sperm through the female reproductive tract.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
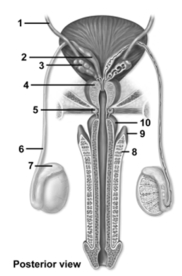 -This figure shows the duct system in the male reproductive tract.Which number indicates the seminal vesicle?
-This figure shows the duct system in the male reproductive tract.Which number indicates the seminal vesicle?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 7
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary oocyte is arrested in
A) prophase I.
B) anaphase I.
C) prophase II.
D) metaphase II.
E) metaphase I.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not part of the vulva?
A) Mons pubis
B) Clitoris
C) Labia majora
D) Labia minora
E) Vagina
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lateral margin of the uterine tube,which bears the fimbriae,is called the
A) ampulla.
B) fornix.
C) isthmus.
D) infundibulum.
E) uterine part.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which cord or sheet of connective tissue attaches to the ovary at the hilum?
A) Suspensory ligament
B) Ovarian ligament
C) Mesovarium
D) Broad ligament
E) Round ligament
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of the dartos and cremaster muscles is to
A) attach the penis to the body wall.
B) produce erections.
C) regulate the temperature of the testes.
D) help the testes descend into the scrotum prior to birth.
E) move sperm along the ductus deferens.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A secondary oocyte arrests in
A) prophase I.
B) anaphase II.
C) prophase II.
D) metaphase II.
E) metaphase I.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The vagina is lined with
A) transitional epithelium.
B) stratified squamous epithelium.
C) ciliated columnar epithelium.
D) simple cuboidal epithelium.
E) pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not correct regarding the ovaries?
A) Each ovary has an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
B) The ovaries are located lateral to the uterus.
C) The ovarian artery and vein join the ovary at its hilum.
D) The gametes develop from the ovarian germinal epithelium.
E) The tunica albuginea is deep to the germinal epithelium.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
As each primary oocyte completes meiosis I,the two cells that form are a secondary oocyte and a _________ _________ (2 words).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rete testis
A) receives sperm from the seminiferous tubules.
B) is the nerve plexus that supplies the testis.
C) is a venous network that cools the arterial blood traveling to the testis.
D) transports seminal fluid to the efferent ductules.
E) is the site of spermiogenesis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sperm are produced in the
A) rete testis.
B) seminiferous tubules.
C) epididymis.
D) seminal vesicles.
E) efferent ductules.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dome-shaped superior portion of the uterus is the
A) body.
B) pylorus.
C) fundus.
D) fornix.
E) isthmus.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 102
Related Exams