B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Imprinting is a type of innate behavior.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A type of behavior that causes babies of many animals to back away from a visual cliff is a(n)
A) innate behavior.
B) habituation.
C) behavior learned by observation.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) learned behavior.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A squirrel visits your bird feeder every day,and has learned that if it jumps onto the feeder,seeds will fall on the ground that it can then eat.The squirrel has gone through which of the following?
A) classical conditioning
B) imprinting
C) habituation
D) operant conditioning
E) observational learning
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sexual dimorphism in humans is most likely due to which of the following?
A) uncertainty of paternity by males
B) competition between males
C) desire for monogamy by females
D) female preference for physically attractive males
E) higher discrimination in mates by males
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals that mark and defend a home range against other animals are exhibiting
A) imprinting.
B) habituation.
C) symbiotic behavior.
D) territorial behavior.
E) taxis behavior.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many small animals,such as raccoons and squirrels,become used to and stop reacting to loud noises,sights,and actions of people in cities or suburbs.They react differently from how they would,if encountering people in the wild.This is an example of
A) habituation.
B) taxis.
C) reflex.
D) observational.
E) imprinting.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Male sticklebacks that are shown a model of a fish with a red belly will attack,thinking it is a breeding male.Model fish without a red belly are not attacked.This is an example of which of the following?
A) reflex
B) fixed action pattern
C) learned behavior
D) taxis
E) imprinting
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A chimp using a stick to probe for termites from a nest is evidence of cognition.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sepia apama cuttlefish mollusk males and females
A) are sexually dimorphic, having different arm lengths and colorations.
B) are opportunistically hermaphroditic, able to mate as either male or female depending on the population needs.
C) mate during the warm spring season.
D) live in populations of equal proportions, producing equal probability of reproductive success.
E) can't mate successfully unless they are among the larger individuals in the population.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eusocial animals like ants,the queen is diploid and the male is haploid.Why would female worker ants be more likely than other animals to engage in altruism,feeding the queen's offspring?
A) The worker ants hope for reciprocal altruism and may become the queen ant.
B) They are more related to the queen's offspring than they would be to their own offspring.
C) It is a reflex for the worker ants to be altruistic.
D) The worker ants are monogamous and remain faithful to the queen ant.
E) The queen establishes a dominance hierarchy over the colony.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An evolutionary mechanism in animals that sacrifices an individual's genes for the sake of the genes it shares with related animals is termed kin selection.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In optimizing foraging,birds often stop feeding in an area and move on,even though there are still some seeds left.What is the best explanation for this observation?
A) They will leave some seeds to create the next generation of plants.
B) Other areas may have food at a lower density.
C) They are more likely to find a mate if they move around.
D) They are safer from predators when moving.
E) The density of the food becomes low, so it will take too much energy to find.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of behavior that does not require learning or experience to be performed correctly is
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) innate behavior.
E) operant conditioning.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A flock of crows attacking a great horned owl is an example of
A) bobbing.
B) cavorting.
C) dribbling.
D) mobbing.
E) stotting.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Reproducing is a type of innate behavior.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
Hanlon,Naud,and their colleagues analyzed DNA among mating males and fertilized eggs of Sepia apama cuttlefish,after mating had been observed.Examine their results in this figure.Which conclusion is supported by these results? 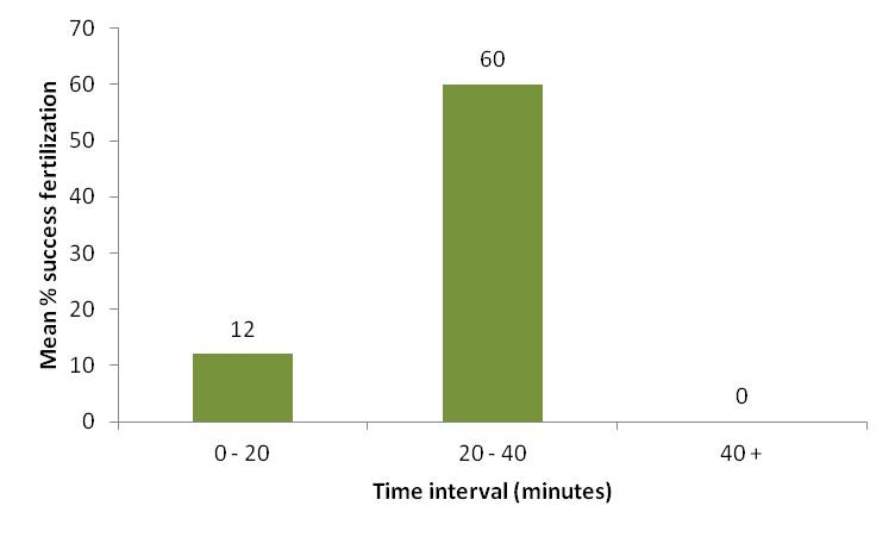
A) Mimicry of females by smaller males does not result in any successful production of fertilized eggs.
B) Guarding females for more than 40 minutes prevents females from sorting and fertilizing sperm and eggs before the eggs die.
C) Smaller males that mimic females are more successful in producing fertilized eggs.
D) There is no reproductive value for a male to guard the female for less than 20 minutes.
E) A male guarding a female 20 to 40 minutes from subsequent mating attempts of other males is the most successful behavior.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 57 of 57
Related Exams