B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that evolution proceeds in small,incremental changes over many generations is
A) temporal equilibrium.
B) gradualism.
C) catastrophism.
D) temporal isolation.
E) punctuated equilibrium.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Grand Canyon,in the southwestern U.S.,there are many species of squirrels,including the Albert Squirrel and a "subspecies," the Kaibab Squirrel (isolation is not complete,according to the biological species definition by Ernst Mayr) .The two populations of squirrels can interbreed to produce fertile offspring,but the populations exist on different portions of the rim of the Grand Canyon,separated by the canyon and the Colorado River.This is an example of
A) sympatric speciation.
B) postzygotic speciation.
C) prezygotic specation.
D) parapatric speciation.
E) allopatric speciation.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 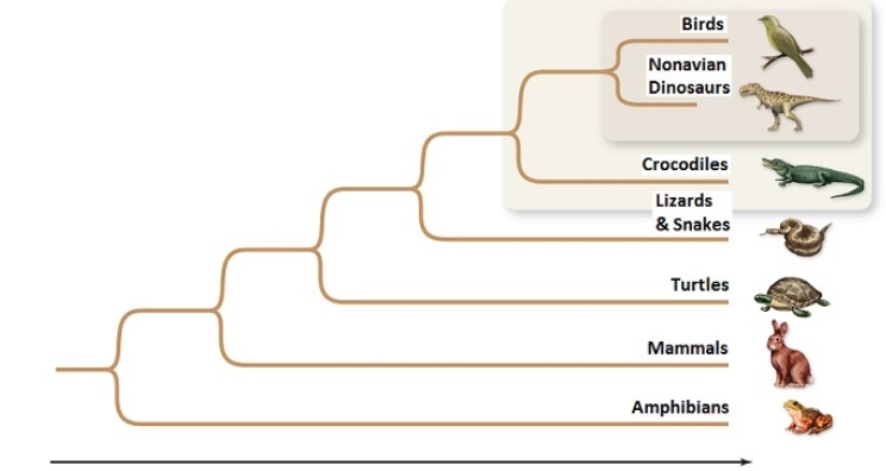 -Starting from the root of a phylogenetic tree,any node that is shown further from the root,than other nodes,means
-Starting from the root of a phylogenetic tree,any node that is shown further from the root,than other nodes,means
A) the species (or groups represented) diverged most recently from a common ancestor.
B) the two species (or groups of species represented) at the furthest node diverged by sympatric speciation.
C) convergent evolution has selected for the species (or groups of species represented) to be similar.
D) the species (or groups of species represented) are in the outgroup.
E) that only those species at the furthest node, from the root, are in a clade.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Formation of a tetraploid plant from two different diploid parental species of plants is an example of ____ speciation.
A) postzygotic
B) prezygotic
C) sympatric
D) parapatric
E) allopatric
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Figuer:  -The outgroup in this cladogram of vertebrate animals is the amphibians.
-The outgroup in this cladogram of vertebrate animals is the amphibians.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:  -From the data shown in the table,what can be concluded about the flower preferences of bumblebees?
-From the data shown in the table,what can be concluded about the flower preferences of bumblebees?
A) They prefer yellow-orange flowers only found in M. lewisii.
B) They prefer red flowers in both species of monkeyflower.
C) They prefer pink flowers in both species of monkeyflower.
D) They prefer M. cardinalis, no matter the color of the flowers.
E) They prefer M. lewisii, no matter the color of the flowers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The speciation that occurred in the islands of the Greater Antilles (i.e.,Cuba,Puerto Rico,Jamaica,and Hispaniola)with lizards called anoles is an example of adaptive radiation.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Systematics utilizes taxonomy and proposed evolutionary relationships to organize life's diversity into groups that reflect evolutionary history.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The types of living organisms on Earth have changed over time,new species have originated,and existing species have disappeared.These are examples of
A) macroevolution.
B) hybridization.
C) speciation.
D) alternation of generations.
E) extinction.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the definition of a biological species,M.lewisii and M.cardinalis can interbreed to produce viable offspring,but are different species for which reason?
A) They live on different continents.
B) If they breed, they do not form fertile offspring.
C) They do not breed in the wild.
D) If they breed, they do not form viable offspring.
E) They do not look alike.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Birds use specific songs,coloring,and mating dances to attract mates of their species (sexual selection) .This is an example of ____ reproductive isolation.
A) allopatric
B) postzygotic
C) prezygotic
D) sympatric
E) parapatric
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Polyploidy is common in _____ species.
A) fungal
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) plant
D) bacterial
E) animal
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By using fossil evidence,paleontologists have concluded that most species exist from _____ years before becoming extinct.
A) 1,000 to 10,000
B) 100 to 1,000
C) 10,000 to 100,000
D) one million to 10 million
E) 100,000 to one million
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A polyphyletic group is a group of species that excludes the most recent common ancestor.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:  -The research by Bradshaw and Schemske supports the hypothesis that a change in just one gene locus may have jump-started speciation in Mimulus.If so,this would be an example of
-The research by Bradshaw and Schemske supports the hypothesis that a change in just one gene locus may have jump-started speciation in Mimulus.If so,this would be an example of
A) gradualism.
B) postzygotic barriers to reproduction.
C) prezygotic barriers to reproduction.
D) punctuated equilibrium.
E) adaptive radiation.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spiny,succulent plants in the Americas are usually in the Cactaceae family,while nearly identical plants in the Mediterranean and northern Africa are in the Euphorbiaceae family.A phylogeny based solely on morphology
A) is the basic definition of the systematics approach called cladistics.
B) requires full identification of all the living and fossil species, before relationships can be assessed.
C) places both the Cactaceae and Euphorbiaceae in the same family clade.
D) establishes an accurate evolutionary link, through ancestry of the cactus and euphorb plants.
E) can lead to proposals of inaccurate relationships, because of convergent evolution.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single common ancestor evolving into the current 28 species of silversword plants found among the Hawaiian islands is an example of
A) adaptive radiation.
B) punctuated equilibrium.
C) extinction.
D) gradualism.
E) a prezygotic barrier to evolution.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sea snail,Littorina saxatilis,is found on the coast of northern Spain.The snails further upshore are large with heavily ridged and banded shells,and share a border with the snails further downshore that are smaller with smooth,unbanded shells.If the upshore and downshore snails were to become separate species,this would be an example of _____ speciation.
A) sympatric
B) parapatric
C) prezygotic
D) allopatric
E) postzygotic
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate of background extinctions is calculated to be _____ species per year per million species.
A) None of the answer choices are correct.
B) 0.001 to 0.01
C) 10 to 100
D) 1.0 to 10
E) 0.1 to 1.0
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 85
Related Exams