A) More information is needed about the couple's parents and grandparents to determine probability.
B) 25%.
C) 0%, because cystic fibrosis is not an inherited illness.
D) 50%.
E) 100%, because both parents are identified as carriers of cystic fibrosis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In pedigree charts,autosomal dominant disorders typically
A) appear only in females.
B) seem to disappear in one generation, only to reappear in the next generation.
C) occur every third generation.
D) appear in every generation.
E) appear only in males.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross RrYy and RRyy pea plants,what percentage of the offspring will have round yellow peas? R = round,r = wrinkled,Y = yellow,y = green.
A) 25%
B) 75%
C) 50%
D) 100%
E) 0%
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A physician reports to you the lab results in identifying your genetic condition relating to your skin health."DNA fingerprint" information indicates that you have two different versions of the allele for a particular skin protein,and this is called
A) heterozygous.
B) dominant.
C) recessive.
D) homozygous.
E) homologous.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diagrams of gene order and spacing on chromosomes are
A) metabolic maps.
B) karyotypes.
C) linkage maps.
D) genotypes.
E) phenotypes.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross two pea plants,one with green peas and the other with yellow peas,you find all of the offspring have yellow peas.You conclude the yellow parent was
A) heterozygous.
B) homozygous for the recessive gene.
C) homozygous for the dominant gene.
D) homozygous for the dominant allele.
E) homozygous for the recessive allele.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Females who are carriers for hemophilia
A) theoretically pass the allele for hemophilia to half of their daughters.
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) theoretically pass the allele for hemophilia to half of their offspring.
D) usually do not show any symptoms of hemophilia.
E) theoretically pass the allele for hemophilia to half of their sons.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A dihybrid cross is a mating between two individuals that are each ______________ for ___________ gene (genes) .
A) heterozygous; two
B) homologous; two
C) homozygous; one
D) homozygous; two
E) heterozygous; one
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adult female bollworm moths lay eggs on cotton bolls.These eggs then hatch,and grow into caterpillars that eat the seeds of the boll.Eggs and sperm would be produced by
A) mitosis.
B) fertilization.
C) meiosis.
D) translocation.
E) crossing over.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Having the alleles Tt is
A) a loci.
B) linkage.
C) a genotype.
D) a phenotype.
E) a gene.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a farmer grows cotton containing the gene for Bt toxin,insects that are resistant (rr) survive and reproduce.This is an example of
A) genetic drift.
B) dominance.
C) natural selection.
D) independent assortment.
E) recombination.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A testcross is a mating of an individual with an unknown genotype and an individual that
A) is homozygous dominant.
B) has a known genotype.
C) is homozygous recessive.
D) is a wild-type.
E) is heterozygous.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a farmer grows cotton containing the gene for Bt toxin,they often leave a strip of non-Bt cotton around the outside of the field for what reason?
A) because the non-Bt cotton grows better
B) because the non-Bt cotton does not drive the moths and caterpillars to extinction
C) to allow the non-Bt and Bt cotton plants to cross pollinate
D) to allow some rr bollworm caterpillars to survive
E) to allow some RR bollworm caterpillars to survive and limit selection pressure for resistance
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gametes may carry different combinations of alleles because of
A) random fertilization and crossing over.
B) random fertilization.
C) random fertilization and alignment of chromosomes.
D) crossing over and random alignment of chromosomes.
E) random alignment of chromosomes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
In these data, the parental generation characteristics (resistant or susceptible) are shown at top. 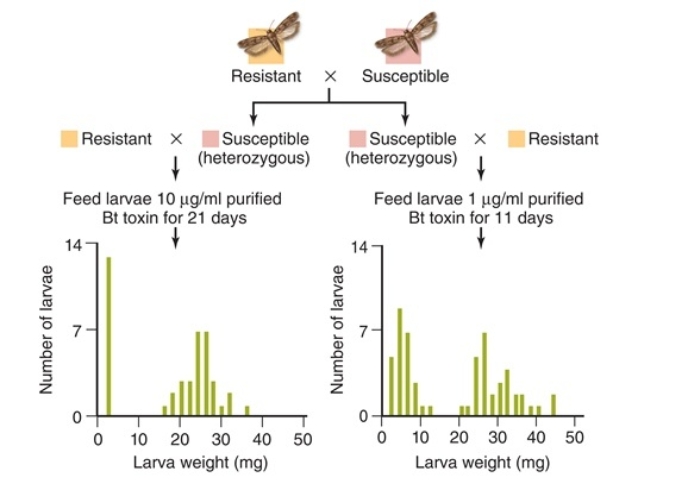 -What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in the figure?
-What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in the figure?
A) Resistance to Bt toxin is dominant.
B) Resistance to Bt toxin is recessive.
C) The size of larvae is dependent on treatment with Bt toxin.
D) Resistance to Bt toxin is not genetic.
E) The number of larvae is dependent on treatment with Bt toxin.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a farmer grows cotton containing the gene for Bt toxin,insects that are resistant (rr) survive and reproduce.These insects were resistant because
A) the insects were able to produce gametes that were resistant to the insecticide.
B) they inherited the alleles that made them resistant.
C) the insecticide caused mutations to generate resistant alleles.
D) the insects wanted to survive the insecticide and mutated their DNA.
E) by random chance some insects did not die from the insecticide.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
X-linked recessive disorders affect more females than males.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between those of the two different homozygotes,this is called
A) epistasis.
B) incomplete dominance.
C) independent assortment.
D) polygenic.
E) codominance.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which gametes can a RrYy plant produce?
A) RY, Ry, rY, or ry
B) Rr or Yy
C) RY or ry
D) R or r
E) RrYy
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross RrYy and RRyy pea plants,what fraction of the offspring will have yellow peas? R = round,r = wrinkled,Y = yellow,y = green.
A) 0%
B) 100%
C) 25%
D) 75%
E) 50%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 99
Related Exams