A) hydrogen bonds between nitrogen base pairs.
B) covalent bonds between nitrogen base pairs.
C) phosphodiester bonds between the deoxyribose sugars.
D) ionic bonds between the phosphate pairs.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transposable elements
A) result from damage to the chromosomes by things like radiation.
B) are DNA sequences that can "jump" within the genome.
C) are another name for translocations.
D) are segments of RNA found in chromosomes.
E) are formed during transcription.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA genetic coding and cell regulation is now understood to be incredibly important to every cell among organisms, and is also associated with viruses. Through the early and mid 1900s, scientists developed new molecular analysis methods that changed the foundations of how we understand "life" to function. Normal health and homeostasis, as well as disease, and natural variations in form and function among organisms are now better understood. Medical and biological applications have increased dramatically with the understanding of DNA molecule structure, and it is helpful to have recognition of the scientists and sequence of events contributing to our understanding. -The scientist (scientists) who was (were) given credit for first determining the molecule structure of DNA by building a ball-and-stick model is (are)
A) Avery and Macleod.
B) Griffith.
C) Chargaff.
D) Watson and Crick.
E) Hershey and Chase.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which proteins initiate transcription in eukaryotes by recognizing sequences within the promoter region of a gene and attracting RNA polymerase?
A) poly A tails
B) TATA boxes
C) transcription factors
D) inducers
E) repressors
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Purine bases have a _________ ___________ structure.
A) triple ring
B) double ring
C) double triangle
D) single triangle
E) single ring
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FOXP2 functions by
A) acting as a neurotransmitter between neurons and muscles in the jaw.
B) regulating the transcription of other genes.
C) regulating cell division.
D) acting as a neurotransmitter between neurons in the ear and brain.
E) regulating mRNA splicing.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because cells are very efficient in the processes that they carry out,very little energy is needed for the cell to make proteins.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How did the researchers estimate that the original FOXP2 mutation happened 300,000-400,000 years ago?
A) by examining the fossil record
B) They found the mutation in Neandertal DNA.
C) They found the mutation in chimpanzee DNA.
D) They found the mutation in 300,000-year-old human remains.
E) using a molecular clock
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The step of translation in which an mRNA,a small ribosomal subunit,and the initiator tRNA are aligned together is 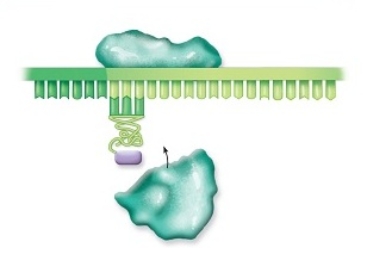
A) termination.
B) initiation.
C) transcription.
D) mitosis.
E) elongation.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:  -What type of mutation has occurred in the following? Normal allele 5'-GGAAUGAAACAGGAACCC-3'
Mutant allele 5'-GGAAUGAAACAGGUACCC-3'
-What type of mutation has occurred in the following? Normal allele 5'-GGAAUGAAACAGGAACCC-3'
Mutant allele 5'-GGAAUGAAACAGGUACCC-3'
A) deletion of one base
B) substitution
C) deletion of two bases
D) insertion of two bases
E) insertion of one base
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transcription and replication occur during ____________________ of the cell cycle.
A) prophase
B) anaphase
C) interphase
D) telophase
E) metaphase
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in a cell's DNA sequence is
A) transcription.
B) a mutation.
C) translation.
D) replication.
E) an operon.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A gene is any DNA sequence that is transcribed to any type of RNA.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A region of a chromosome contains two strands of DNA,yet only one is used to transcribe a gene because
A) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, which precedes the gene only on the template strand of DNA.
B) the start of transcription is random along the chromosome and doesn't always occur on a gene.
C) RNA polymerase binds to the terminator, stopping transcription on one strand of DNA.
D) all genes are found on the same strand of DNA in a chromosome.
E) both strands are transcribed, but only one strand of DNA contains a reading frame.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A germline mutation occurs in cells that give rise to
A) gametes.
B) diploid cells.
C) skin cells.
D) liver cells.
E) nonsex cells.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA genetic coding and cell regulation is now understood to be incredibly important to every cell among organisms, and is also associated with viruses. Through the early and mid 1900s, scientists developed new molecular analysis methods that changed the foundations of how we understand "life" to function. Normal health and homeostasis, as well as disease, and natural variations in form and function among organisms are now better understood. Medical and biological applications have increased dramatically with the understanding of DNA molecule structure, and it is helpful to have recognition of the scientists and sequence of events contributing to our understanding. -The scientist (scientists) who showed that DNA contained equal amounts of certain nitrogen bases is (are)
A) Griffith.
B) Avery and Macleod.
C) Chargaff.
D) Hershey and Chase.
E) Wilkins and Franklin.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells,sequences of mRNA that are removed from an mRNA molecule before being translated are
A) anticodons.
B) introns.
C) terminators.
D) exons.
E) proteomes.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cystic fibrosis may be caused by a protein that does not fold correctly into its final form.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "Central Dogma" refers to
A) passage of genetic information from RNA to specific proteins by transcription.
B) inheritance of DNA genetically controlled traits from parents to offspring in every organism.
C) the similarity of the energy molecule ATP to the nucleotides in DNA.
D) the flow of genetic information in cells, from DNA genes to specific proteins.
E) passage of genetic information from DNA to RNA by translation.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA genetic coding and cell regulation is now understood to be incredibly important to every cell among organisms, and is also associated with viruses. Through the early and mid 1900s, scientists developed new molecular analysis methods that changed the foundations of how we understand "life" to function. Normal health and homeostasis, as well as disease, and natural variations in form and function among organisms are now better understood. Medical and biological applications have increased dramatically with the understanding of DNA molecule structure, and it is helpful to have recognition of the scientists and sequence of events contributing to our understanding. -The technique that allowed Hershey and Chase to show that the bacteriophage injects a specific molecule,was to
A) apply X-ray diffraction to detect whether protein or DNA was injected into a bacterium.
B) tag both DNA and protein with radioactive markers, to identify which was injected into a bacterium.
C) tag DNA in the virus with radioactive phosphorus, to identify if it as injected into a bacterium.
D) apply heat to the polysaccharide of the bacterium, then determine if protein or DNA was responsible for infection.
E) tag protein with radioactive sulfur, to identify if it was injected into a bacterium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 77
Related Exams