A) phagocytosis
B) facilitated diffusion
C) neither osmosis nor facilitated diffusion
D) pinocytosis
E) osmosis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Once ATP donates its phosphate to a coupled reaction it becomes ADP.The ADP
A) can be recharged in an exergonic reaction to form ATP.
B) is a waste product that must be broken down.
C) can be recharged in an endergonic reaction to form ATP.
D) becomes the needed potential energy source for another coupled reaction.
E) can be recharged in an oxidation reaction to form ATP.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxidation and reduction reactions are typically linked within a cell. They are part of most matter and energy transformations necessary for vital life function. -Oxidation means
A) the loss of electrons from a molecule.
B) the loss of oxygen by a cell.
C) the gain of electrons by a molecule.
D) the gain of oxygen by a cell.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecular reactants for photosynthesis are
A) glucose and carbon dioxide.
B) glucose and sunlight.
C) organic compounds.
D) glucose and water.
E) water and carbon dioxide.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Movement of molecules down a concentration gradient is an example of
A) reduction.
B) kinetic energy.
C) active transport.
D) oxidation.
E) potential energy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these membrane transport processes does not require membrane proteins?
A) active transport pumps
B) facilitated diffusion
C) endocytosis
D) osmosis
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Phagocytosis is a process that cells use to move materials in through the cell membrane.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A serving of 30 grams of almonds may have 190 Calories listed on a nutrition label.This represents
A) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 grams of water 1 °C.
B) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 grams of water 190 °C.
C) enough energy to raise the temperature of 30 kilograms of water 190 °C.
D) enough energy to raise the temperature of 190 kilograms of water 1 °C.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is not part of the first law of thermodynamics?
A) The amount of energy in the universe is constant.
B) None of the answer choices are correct.
C) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
D) Energy can be converted to other forms of energy.
E) Any energy transformation loses some energy to its surroundings as heat.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cholera is a bacterial disease, in which fatal dehydration can occur due to loss of water into the intestines. Cystic fibrosis is a human genetic disease characterized by excess mucus buildup on the linings of the lungs, making breathing difficult. Cholera acts on intestine cells to force water transport out of the cells and the body. Cystic fibrosis has an abnormal CFTR transport protein that limits water transport out of the cells and the body. -How does the bacteria that causes cholera,Vibrio cholera,trigger potentially life-threatening diarrhea?
A) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
B) Cholera toxin inhibits CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
C) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to decreased transport of water into the intestines.
D) Cholera toxin stimulates CFTR leading to increased transport of water into the intestines.
E) Cholera toxin causes a DNA genetic mutation that modifies the function of CFTR proteins.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An endergonic reaction is a reaction that is characterized by
A) yielding larger product molecules than the original reactants.
B) yielding smaller product molecules than the original reactants.
C) having products with lower energy than the reactants.
D) having products with higher energy than the reactants.
E) often having higher energy in product molecules than the reactants, and yielding larger product molecules.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
This diagram summarizes energy transfers and molecule exchanges among plants and animals, as you will learn later we call producers and consumers. 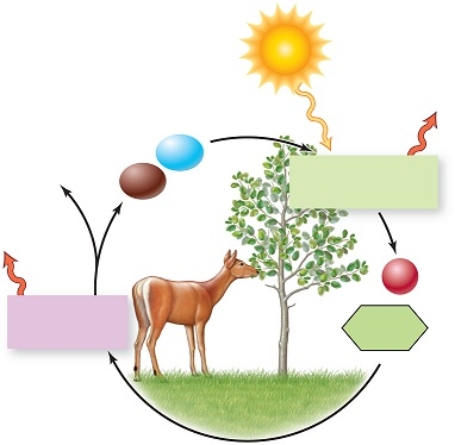 -Plants require energy to perform photosynthesis,in which glucose is formed from carbon dioxide and water,and stores energy.This is a(n) _____ reaction.
-Plants require energy to perform photosynthesis,in which glucose is formed from carbon dioxide and water,and stores energy.This is a(n) _____ reaction.
A) kinetic energy
B) exergonic
C) endergonic
D) potential energy
E) equilibrium
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The metabolic rate of individuals is influenced by
A) the amount of body fat.
B) the amount of thyroxin produced by the thyroid.
C) age.
D) All of the answer choices are correct.
E) weight.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.  -The molecule that fits into the active site of an enzyme and reacts with the enzyme is
-The molecule that fits into the active site of an enzyme and reacts with the enzyme is
A) an analog.
B) a substrate.
C) always a carbohydrate.
D) always broken down by the enzyme.
E) always a protein.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Much medical advice towards heart health indicates that you should eat less sodium (table salt) .Notable higher risks of high sodium may include high blood pressure and damage to arteries or organs in your body.If you eat a single meal with large amounts of salt to suit your taste,which of these may result within minutes,as the sodium enters your bloodstream?
A) Simple diffusion of water and sodium will both balance in an isotonic condition between arteries and body tissues.
B) You should expect no change in the concentration gradient because of a single meal, rather than lifestyle and diet.
C) Your blood will become hypotonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.
D) Your blood will become hypertonic, and water in your body tissues will flow into your arteries, inflating them.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine which of these statements best summarizes the cellular regulation of concentration gradients.
A) Enzymes are used in the cell to build molecules on one side of membranes to establish concentration gradients.
B) Passive and active transport both function when vesicles transport materials across the cell membranes.
C) Membrane phospholipids and proteins regulate transport functions to establish concentration gradients or equilibria.
D) Selective permeability of the cell membranes results in equal amounts of substances inside and outside the cell.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
This diagram shows the basic structure and function of an enzyme, acting to catalyze a cell's chemical reaction.  -The region of an enzyme that catalyzes reactions is called a(n)
-The region of an enzyme that catalyzes reactions is called a(n)
A) active site.
B) binding pocket.
C) catalyst site.
D) reaction site.
E) cofactor site.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phagocytosis of an infective bacterium by a white blood cell is a subset type of
A) exocytosis.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) simple diffusion.
D) endocytosis.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does phenylalanine accumulate in patients with phenylketonuria?
A) They lack an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.
B) They produce too much phenylalanine.
C) They lack an enzyme to produce phenylalanine.
D) They lack an inhibitor of an enzyme to break down phenylalanine.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For animals and other organisms consuming food,the molecular reactants to cellular respiration are
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) entropy.
C) digestive enzymes.
D) glucose and oxygen.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 78
Related Exams