A) positive feedback.
B) denaturation.
C) negative feedback.
D) equilibrium.
E) a coenzyme.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the environment surrounding a cell has a lower concentration of solute than the cell,the
A) environment is hypotonic to the cell.
B) environment is isotonic to the cell.
C) cell will not experience a net gain or loss of water.
D) environment is hypertonic to the cell.
E) cell will die.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Coupled reactions are reactions in which a
A) exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction.
B) exergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
C) endergonic reaction drives an exergonic reaction.
D) endergonic reaction drives a spontaneous reaction.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Up to 25% of a cell's ATP is used to run sodium-potassium pumps. Without the resulting sodium and potassium gradients, neurons and muscles cannot fire properly. -If a person is poisoned with cyanide,they cannot generate ATP,and die within a few minutes.In relation to the sodium-potassium pump,what specific impact would cyanide have on concentrations across the cell membrane?
A) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher inside the cell.
B) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would become isotonic outside the cell.
C) Sodium concentration would be higher outside the cell, while potassium concentration would be higher inside the cell.
D) Sodium and potassium concentrations would both be higher outside the cell.
E) Both sodium and potassium concentrations would reach equilibrium conditions across the cell membrane.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way to produce a vaccine is to heat a virus or bacteria and then inject the inactive pathogen as a vaccination.How would the heat inactivate a virus?
A) by denaturing proteins
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) by inhibiting its metabolism
D) by blocking facilitated diffusion
E) by destroying the membrane
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 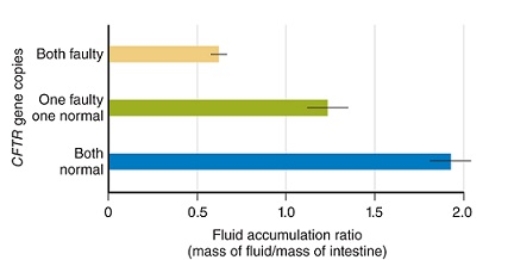 -What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in this figure?
-What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in this figure?
A) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, fewer copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.
B) The number of defective CFTR genes did not correlate with resistance to cholera toxin.
C) The fewer copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
D) The more copies of a defective CFTR gene an organism has, the more resistant it is to cholera toxin.
E) The more cholera toxin an organism was exposed to, the more copies of its CFTR gene that became defective.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
You are cold.Your body begins a shivering response.You quickly rub your hands together,and the friction produces a small amount of heat.The heat is evidence of increasing entropy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable (biological) membrane is
A) osmosis.
B) active transport.
C) always beneficial to a cell.
D) a rare occurrence.
E) a process that always requires proteins.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enzymes speed chemical reactions by
A) supplying energy to the reaction process.
B) raising the temperature of the surroundings.
C) lowering the amount of reactants that are needed.
D) lowering the energy required to start a chemical reaction.
E) maintaining chemical equilibrium.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A raw peanut having almost 2 Calories of energy has 2,000 times the energy to raise the temperature of 1 gram water by 1 °C.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of kinetic energy?
A) sound
B) light
C) heat
D) the energy in chemical bonds
E) random molecular movement
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Reduction is the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Noncompetitive inhibition of enzymes occurs
A) when a cofactor, instead of a reactant, binds to the enzyme active site.
B) when a substance binds to an enzyme at a site away from the active site.
C) by blocking the production of an enzyme.
D) when a substance other than the substrate binds at the active site of an enzyme.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Simple diffusion
A) does not require energy.
B) utilizes proteins to move molecules across a membrane.
C) requires energy.
D) cannot occur without a membrane present.
E) moves molecules against a concentration gradient.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Each protein in an electron transport chain is sequentially oxidized,then reduced,allowing the work of actively transporting oxygen molecules by active membrane transport.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme is
A) always a protein.
B) an organic molecule that catalyzes a cellular reaction.
C) not necessary to sustain life in a cell.
D) used up in a reaction.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An enzyme is a lipid that catalyzes chemical reactions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Turgor pressure in plant cells is
A) a result of the walled cell being in a hypotonic environment.
B) due in part to osmosis.
C) necessary to keep plants from wilting.
D) the force of water against the inside of the cell wall.
E) All of the answer choices are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 78 of 78
Related Exams