A) G1 phase - DNA replication
B) G2 phase - preparation for meiosis
C) S phase - DNA replication
D) M phase - cell growth
E) G0 phases - cell growth
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure is formed by two sister chromatids being held together by a centromere?
A) chromosome
B) chromatin
C) histones
D) nucleosome
E) DNA
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells that do not receive the correct signals to move from G1 into S phase will enter G0 and therefore will
A) immediately move into the mitotic phase.
B) never be able to undergo mitosis.
C) be able to produce gametes through meiosis.
D) stay in an undifferentiated state and become stem cells.
E) not undergo mitotic division unless it later receives the go ahead signal.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell is inhibited during the S phase of its cycle.It will not reproduce due to lack of
A) ATP availability.
B) centriole migration.
C) centromere formation.
D) DNA synthesis.
E) plasma membrane structure.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rick had a high incidence of cancer in his family.Four of the following five statements are preventative measures to avoid cancer.Which of the following is not correct?
A) Increase consumption of foods rich in vitamin A and C.
B) Avoid salt-cured,pickled,or smoked foods.
C) Increase consumption of vegetables from the cabbage family.
D) Avoid cigarette smoking,smokeless tobacco,and sunbathing.
E) Avoid a high fiber,low sodium diet.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below.Differentiated cells,such as nerve cells,would be in which of the following stages of the cell cycle? 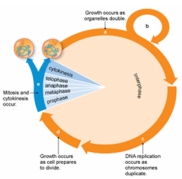
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While Jeff was looking under the microscope at cells in different stages of mitosis he commented on the fact that many cells were in the same stage.If you were looking under the compound light microscope at an onion root tip,what stage would the majority of the cells be in the cell cycle?
A) anaphase
B) metaphase
C) cytokinesis
D) interphase
E) prophase
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which stage of the cell cycle do the chromosomes duplicate?
A) interphase: S
B) interphase: G1
C) interphase: G2
D) prophase
E) telophase
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of cancer cells?
A) stimulate the growth of blood vessels
B) travel through the bloodstream to other parts of the body
C) exhibit contact inhibition
D) have abnormal chromosomes
E) produced by a mutation of a proto-oncogene
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tumor suppressor gene undergoes a mutation that causes it to lose its normal function.What would be the most likely result of this mutation?
A) The cell cycle halts and reverses back to the G0 stage.
B) The cell cycle undergoes contact inhibition even when it is not surrounded by other cells.
C) The cell cycle accelerates.
D) The cell no longer responds to signals that cause it to stop dividing or undergo apoptosis.
E) The cell stops dividing permanently and will never re-enter the cell cycle.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is NOT a correct association?
A) interphase-shortest stage of the cell cycle
B) S stage-DNA synthesis
C) M stage-mitosis and cytokinesis
D) G1 stage-cell grows in size and cell organelles increase in number
E) G2 stage-metabolic preparation for mitosis
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cancer will occur if one copy of a mutant tumor suppressor gene is inherited.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytokinesis usually,but not always,follows mitosis.If a cell undergoes mitosis and not cytokinesis,this would result in
A) a cell with a single large nucleus.
B) a cell with two or more nuclei.
C) cells with abnormally small nuclei.
D) feedback responses that prevent mitosis.
E) death of the cell line.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measurements of the amount of DNA per nucleus were taken on a large number of cells from a growing fungus.The measure of DNA levels ranged from three to six picograms per nucleus.One nucleus had five picograms of DNA.What stage of the cell cycle was the nucleus in?
A) G0
B) G1
C) S
D) G2
E) M
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The drug chloral hydrate prevents elongation of microtubules by preventing the addition of new subunits to the growing end.During which stage of mitosis would chloral hydrate be most harmful?
A) prophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) telophase
E) interphase
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multicellular organisms undergo mitotic cell division to
A) produce new organisms.
B) produce gametes.
C) increase the variability of the population.
D) increase the size of the organism.
E) facilitate sexual reproduction.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nuclear division is represented in the figure below by the letter 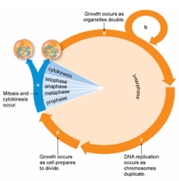
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Apoptosis occurs when
A) a cell lyses due to an imbalance in water uptake.
B) white blood cells attack damaged cells and destroy them.
C) the controls over cell division are lost and a tumor forms as the mass of cells grow.
D) a cell with damaged DNA stops working and dies.
E) a damaged cell is programmed to fragment and then is phagocytized.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rebecca found out that she has a mass of dividing cells called a tumor in her ovaries.She has had tests and is returning to the doctor.What would the best results the doctor could tell her be?
A) It is a benign tumor.
B) The cells are cancerous and are in situ.
C) It is a malignant tumor.
D) It is malignant ovarian cancer.
E) The tumor has metastasized and invaded neighboring tissue.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A protein that promotes apoptosis would be considered a(n)
A) oncogene.
B) proto-oncogene.
C) tumor suppressor.
D) mutant tumor suppressor.
E) signal transduction pathway protein.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 90
Related Exams