A) an economic profit,and also one in the long run.
B) a normal profit,but in the long run only an economic profit.
C) economic profits or losses,but in the long run only a normal profit.
D) economic profits or losses,but in the long run only an economic profit.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The variety of products and product features that consumers may choose from in monopolistically competitive industries:
A) at least partially offsets the economic inefficiencies of this market structure.
B) leads to an optimal allocation of resources in the market structure.
C) guarantees that firms produce at full-capacity output levels.
D) makes the demand curves facing firms in these industries more elastic.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) behaves in many ways like an international cartel.If the cartel were to hire a consulting firm to monitor the production rates of member countries,the economic reason for this monitoring is to:
A) make sure that each member country is producing at an output level at which price equals marginal cost.
B) make sure all the member countries produce at least their quotas so that there will be no oil shortage.
C) detect those member countries that are depressing prices by producing more than their assigned quotas.
D) make sure that the marginal revenue for the last barrel of oil sold by each member country is less than its price.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An oligopolistic price leader increases the price of its product.If all other firms follow the leader's example,the price leader will:
A) decrease its price.
B) increase its price.
C) maintain its new price.
D) increase its quantity of output.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that in a monopolistically competitive industry,firms are earning economic profit.This situation will:
A) reduce the excess capacity in the industry as firms expand production.
B) attract other firms to enter the industry since the barriers to entry are low.
C) cause firms to standardize their product to limit the degree of competition.
D) make the industry allocatively efficient as each firm seeks to maintain its profits.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
OPEC is a classic example of a kinked-demand curve oligopoly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph depicts a monopolistically competitive firm. 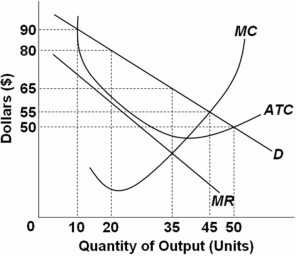 Refer to the above graph representing an individual firm.In the short run,this monopolistically competitive firm will set price at:
Refer to the above graph representing an individual firm.In the short run,this monopolistically competitive firm will set price at:
A) $65 and produce 45 units of output.
B) $65 and produce 35 units of output.
C) $50 and produce 35 units of output.
D) $50 and produce 50 units of output.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary aluminum industry in the United States would be described by an economist as:
A) pure monopoly.
B) pure competition.
C) oligopoly.
D) monopolistic competition.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In competing with rivals,oligopolistic firms will tend to use:
A) price cuts because they do not add to costs like advertising.
B) advertising because it is less easily duplicated than price cuts.
C) collusion because it is a legal way to increase market share.
D) price wars because they will increase the profits of firms.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at a short-run output level where average total cost is $10.00,marginal cost is $5.00,marginal revenue is $6.00,and price is $12.00.In the short run,the firm should:
A) decrease the level of output.
B) increase the level of output.
C) make no change in the level of output.
D) increase product price.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
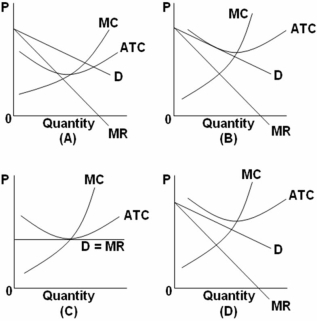 Refer to the above graphs.Which graph would not be a possible depiction of short-run or long-run outcomes for a monopolistically competitive firm?
Refer to the above graphs.Which graph would not be a possible depiction of short-run or long-run outcomes for a monopolistically competitive firm?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The downward-sloping demand curve of a monopolistic competitor:
A) reflects product differentiation.
B) becomes horizontal in the long run.
C) indicates collusion among the members of the product group.
D) ensures that the firm will produce at minimum average cost in the long run.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
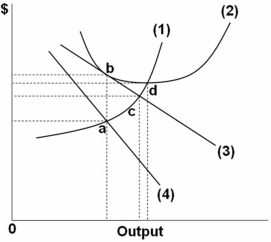 Refer to the above graph of the representative firm in monopolistic competition.Demand is tangent to average total cost at point:
Refer to the above graph of the representative firm in monopolistic competition.Demand is tangent to average total cost at point:
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If an oligopolist's competitors follow its price cuts but ignore its price increases,the oligopolist will face a gap in its marginal revenue schedule.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistically competitive firms are productively inefficient because production occurs where:
A) marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
B) marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.
C) average total cost is greater than the minimum average total cost.
D) average total cost is less than the difference between average total cost and average variable cost.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose some firms exit a monopolistic competition industry.We would expect the demand curve of a firm already in the industry to:
A) shift to the left.
B) shift to the right.
C) become more elastic.
D) remain the same since entering firms serve other customers in the market.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mutual interdependence means that:
A) product differentiation exists,that is,firms produce close substitutes but not identical products.
B) each seller faces a completely inelastic demand curve.
C) each firm must consider the possible reactions of rivals when establishing price policy.
D) when a pure monopolist chooses a price,it also necessarily chooses some specific level of output.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a particular bank regularly announces changes in its interest rate schedules before its competitors,which then set rates very close to those announced by that bank,this could be described as:
A) markup pricing.
B) predatory pricing.
C) price leadership.
D) explicit price collusion.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cigarette industry in the United States would be an example of a:
A) duopoly.
B) noncollusive oligopoly.
C) homogeneous oligopoly.
D) differentiated oligopoly.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A feature of monopolistic competition is:
A) a patent-protected product.
B) homogeneous or standardized products.
C) considerable control over price.
D) nonprice competition.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 179
Related Exams