A) demand conditions
B) ethnocentrism
C) barriers to entry
D) governmental regulation
E) suppliers
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
firm's profit potential and control over marketing activities __________ as it moves from exporting to direct investment as a global market-entry strategy.
A) becomes more stable
B) increases
C) levels off
D) decreases
E) becomes more unpredictable
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
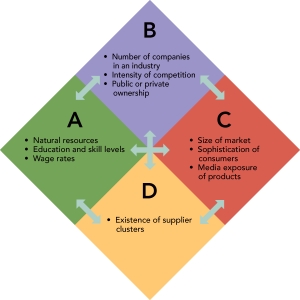 Figure 7-2
-According to Michael Porter's diamond in Figure 7-2 above,quadrant "D" represents
Figure 7-2
-According to Michael Porter's diamond in Figure 7-2 above,quadrant "D" represents
A) factor conditions.
B) related and supporting industries.
C) demand conditions.
D) managerial conditions.
E) company strategy, structure, and rivalry.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
clandestine collection of trade secrets or proprietary information about a company's competitors is referred to as
A) trade piracy.
B) transnational fraud.
C) economic espionage.
D) competitive duplicity.
E) transnational espionage.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning currency exchange rates is most accurate?
A) Fluctuations in exchange rates among the world's currencies are of critical importance in global marketing.
B) Fluctuations in exchange rates among the world's currencies are of minor importance in global marketing.
C) Exchange rate fluctuations are relatively rare, but they usually have serious long-term consequences.
D) Exchange rate fluctuations are almost nonexistent due in great part to the euro.
E) Exchange rate fluctuations may affect the financial sector but rarely reach the consumer.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about world trade flows is most accurate?
A) The EU (European Union) is the world leader in terms of GDP (gross domestic product) .
B) The relative position of the United States as a supplier to the world has increased because of an absolute growth in exports.
C) The United States is running a continuing trade surplus because it has the world's largest gross domestic product.
D) The United States' relative role as an exporter remains strong in the area of aerospace.
E) During the past 30 years, the relative position of the United States in terms of GDP has remained stable despite the fact that actual value of products and services has increased.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic Espionage Act
A) allows the World Court in The Hague to adjudicate trade disputes on behalf of United Nations' members and requires the home country to impose any penalties.
B) imposes a personal fine on a convicted U.S. citizen of up to $10 million.
C) targets espionage activities that are commonplace in any industry that holds governmental contracts.
D) makes the theft of trade secrets by foreign entities a federal crime in the United States.
E) is well-intended in theory, but is virtually impossible to enforce.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the World Trade Organization (WTO) is most accurate?
A) The WTO is a permanent institution that sets rules governing trade between its members.
B) The WTO sets rules governing trade between its members and the remainder of the world.
C) The 153 member countries of the WTO account for approximately 55 percent of world trade.
D) The WTO uses panels of trade experts who can issue non-binding recommendations.
E) The WTO was formed by the United Nations.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Coca-Cola,Gillette razors,and Wrigley's gum are virtually selling the same product in other countries.This is an example of which type of international product strategy?
A) product customization
B) product adaptation
C) product extension
D) product integration
E) product invention
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indirect exporting refers to
A) offering the right to a trademark, patent, trade secret, or similarly valued item of intellectual property in return for a royalty or fee.
B) contracting with a foreign firm to manufacture products according to stated specifications.
C) the combined investment of a foreign country and a local firm to create a local business.
D) when a firm sells its domestically produced goods in a foreign country through an intermediary.
E) when a firm sells its domestically produced goods in a foreign country without intermediaries.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mars,America's second-largest candy company,began doing business in Russia in the late 1980s.The Snickers bar is one of the top selling candies in Russia and is marketed in much the same way as it is in the United States.Mars is most likely a(n) __________ firm.
A) international
B) multidomestic
C) transnational
D) meganational
E) multinational
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dumping refers to
A) illegally disposing of unusable or damaged goods to avoid paying removal fees and/or taxes.
B) when a firm sells damaged or unsalable goods below their original production cost.
C) when a firm sells quality goods at significantly lower prices for the primary purpose of reducing inventory to make room for seasonal goods.
D) when a firm sells quality goods at significantly lower prices for the primary purpose of reducing inventory to make room for newer or more expensive models.
E) when a firm sells a product in a foreign country below its domestic price or below its actual cost.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
a U.S.airplane manufacturer sells its airplanes to business executives in Germany without using intermediaries,it is referred to as
A) direct exporting.
B) indirect exporting.
C) licensing.
D) foreign manufacturing.
E) foreign assembly.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
study of similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations or societies is referred to as __________.
A) market synthesis
B) cross-cultural analysis
C) international sociographics
D) transnational anthropology
E) multicultural ethnocentrism
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
type of exporting has the least amount of commitment and risk but will probably return the least profit?
A) direct
B) indirect
C) licensing
D) joint venture
E) direct investment
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
country's communication,transportation,financial,and distribution systems are considered to be its
A) capital infrastructure.
B) fixed-asset infrastructure.
C) economic infrastructure.
D) geopolitical network.
E) network infrastructure.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an element of related and supporting industries?
A) media exposure of products
B) existence of supplier clusters
C) sophistication of consumers
D) intensity of competition
E) aggregation of markets
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Those in favor of protectionism advocate that protectionism
A) helps reduce tariffs and quotas.
B) encourages the development of domestic industries.
C) encourages economic reliance on foreign countries.
D) creates opportunities for the outsourcing of domestic jobs.
E) creates a more favorable environment for a global economy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Malaysian government recently exchanged 20,000 tons of rice for an equivalent amount of Philippine corn.This is an example of (a)
A) competitive advantage.
B) countertrade.
C) balance of trade.
D) quota.
E) trade feedback.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
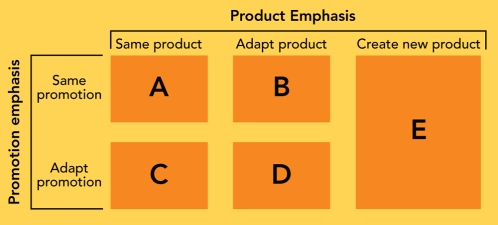 Figure 7-6
-Global companies have five strategies for matching products and their promotion efforts to global markets.According to Figure 7-6 above,"D" refers to which type of strategy?
Figure 7-6
-Global companies have five strategies for matching products and their promotion efforts to global markets.According to Figure 7-6 above,"D" refers to which type of strategy?
A) product extension strategy
B) product adaptation strategy
C) dual adaptation strategy
D) product invention strategy
E) communication adaptation strategy
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 338
Related Exams