A) Converging
B) Diverging
C) Reverberating
D) Parallel-after-discharge
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Transmission of nerve impulses along myelinated axons requires more energy than transmission along unmyelinated axons.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What cell type does number 2 indicate?
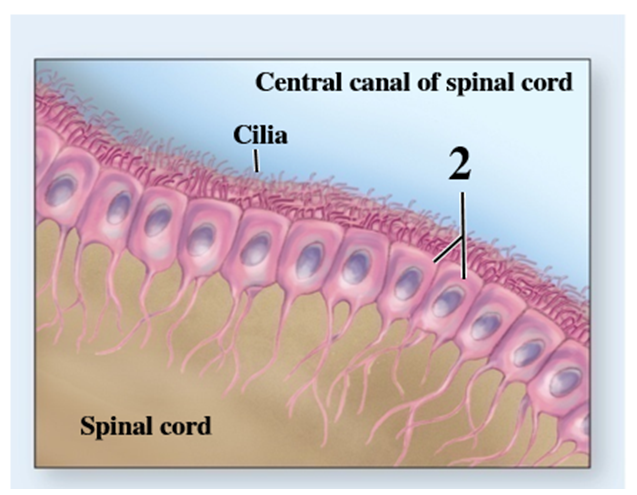
A) Satellite cell
B) Neuron
C) Microglial cell
D) Astrocyte
E) Ependymal cell
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not one of the three common structural types of synapses?
A) Axonucleic
B) Axoaxonic
C) Axosomatic
D) Axodendritic
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Billions of CNS interneurons are grouped in complex patterns called neuronal
A) networks.
B) complexes.
C) pools.
D) meshes.
E) webs.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which glial cell has perivascular feet that wrap around capillaries in the CNS?
A) Astrocyte
B) Ependymal cell
C) Neurolemmocyte
D) Microglial cell
E) Oligodendrocyte
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This condition involves progressive demyelination of neurons in the CNS accompanied by the destruction of oligodendrocytes.As a result,the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted,leading to impaired sensory perception and motor coordination.
A) Guillain-Barré syndrome
B) Parkinson disease
C) Multiple sclerosis
D) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which glial cell defends the body against pathogens?
A) Astrocyte
B) Ependymal cell
C) Neurolemmocyte
D) Microglial cell
E) Oligodendrocyte
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
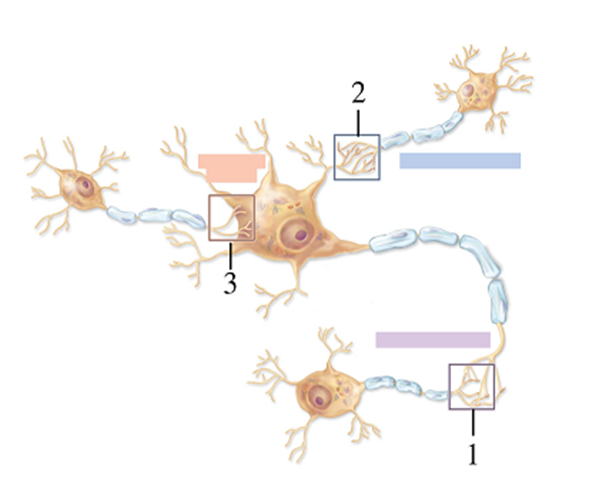 -What type of synapse does number 2 indicate?
-What type of synapse does number 2 indicate?
A) Axodendritic
B) Axoaxonic
C) Axosomatic
D) Dendrodendritic
E) Dendrosomatic
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a function of the motor division of the nervous system?
A) Conducts output (nerve impulses) from the CNS
B) Transmits impulses to muscles and glands
C) Transmits impulses from the viscera
D) Voluntary control of skeletal muscle
E) Involuntary control of the heart
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure depicts a typical nerve.What is indicated by number 2?
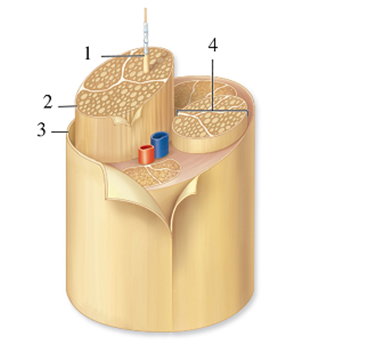
A) Myelin sheath
B) Dendrites
C) Fascicle
D) Epineurium
E) Perineurium
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure does number 5 indicate?
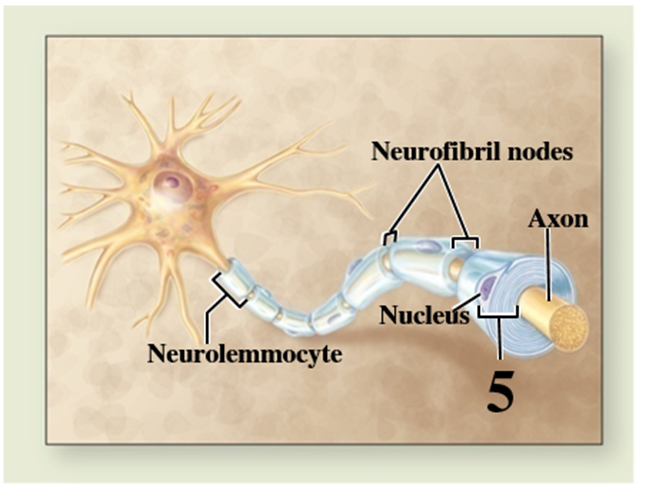
A) Neurofibril node
B) Myelin sheath
C) Nucleus
D) Perivascular foot
E) Ependymal cell
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A condition in which the brain is substantially missing is
A) spina bifida.
B) amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
C) muscular dystrophy.
D) anencephaly.
E) cerebral palsy.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The endoneurium is composed of
A) dense regular connective tissue.
B) simple squamous epithelium.
C) dense irregular connective tissue.
D) areolar connective tissue.
E) pseudostratified nonkeratinized epithelium.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of neuronal circuit that ensures that we continue to breathe while asleep is a _____________ circuit.
A) converging
B) diverging
C) reverberating
D) parallel-after-discharge
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is correct concerning the terms afferent and efferent with respect to the nervous system?
A) Afferent refers to the conduction of an impulse outward from the CNS.
B) Both terms refer to conducting impulses outward from the CNS although efferent pathways carry only sensory impulses.
C) Efferent refers to the conduction of motor impulses toward the CNS.
D) Afferent refers to the conduction of sensory impulses toward the CNS.
E) Both terms refer to conducting impulses toward the CNS although afferent pathways carry only motor impulses.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A secondary tumor is one that originates in one site but subsequently spreads to another site.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What type of synapse does number 1 indicate?
-What type of synapse does number 1 indicate?
A) Axodendritic
B) Axoaxonic
C) Axosomatic
D) Dendrodendritic
E) Dendrosomatic
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the answer that correctly lists,in chronological order,the events involved in synaptic transmission. A: A nerve impulse reaches the synaptic knob B: Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft C: A nerve impulse begins in the postsynaptic cell D: Neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic cell E: A voltage change occurs in the postsynaptic cell
A) a,c,b,d,e
B) a,b,e,d,c
C) c,b,d,e,a
D) a,b,d,e,c
E) c,a,b,d,e
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the most common structural type of synapse?
A) Dendrodendritic
B) Axoaxonic
C) Axosomatic
D) Axodendritic
E) Axonucleic
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 96
Related Exams