A) does not increase equilibrium output or the price level.
B) increases equilibrium output above Y1,but does not change the price level.
C) increases the price level above P1,but does not change equilibrium output.
D) increases equilibrium output above Y1 and decreases the price level below P1.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Lucas supply function,in combination with the assumption that expectations are rational,change in government policy can affect real output only if
A) the policy change is correctly anticipated by the public.
B) the policy change is a surprise.
C) the policy change is a mix of both fiscal and monetary policy changes.
D) expansionary policy changes are made.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetarists and Keynesians
A) disagree on the speed at which wages change.
B) agree on the impact of fiscal policy on the economy.
C) disagree on how the Fed changes money supply.
D) agree on the usefulness of discretionary policy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The curve that assumes that there is some tax rate beyond which the supply response is large enough to lead to a decrease in tax revenue for further increases in the tax rate is the
A) aggregate supply curve.
B) Lucas supply curve.
C) aggregate production function.
D) Laffer curve.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 18.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
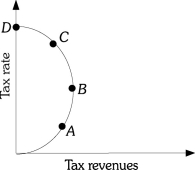 Figure 18.3
-Refer to Figure 18.3.A decrease in tax rates will definitely decrease tax revenue if the economy is at a point such as ________ on the Laffer Curve.
Figure 18.3
-Refer to Figure 18.3.A decrease in tax rates will definitely decrease tax revenue if the economy is at a point such as ________ on the Laffer Curve.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) both A and B
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 18.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
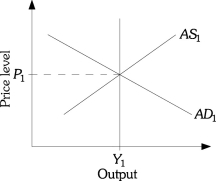 Figure 18.1
-Refer to Figure 18.1.According to the new classical economists,under rational expectations an expected decrease in government spending would
Figure 18.1
-Refer to Figure 18.1.According to the new classical economists,under rational expectations an expected decrease in government spending would
A) shift AS1 to the right.
B) shift AD1 to the right.
C) shift AD1 to the left.
D) not change AD and AS.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetarists argue that the money supply should
A) grow at a rate equal to the average growth of real output.
B) grow at a rate slower than the average growth of real output.
C) grow at a rate greater than the average growth of real output.
D) be held constant over the business cycle.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With the Lucas supply function,a price surprise means
A) actual price is greater than expected price.
B) actual price is less than expected price.
C) actual price equals expected price.
D) actual price is either greater than or lower than expected price.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is difficult to test whether the velocity of money is constant over time because
A) there has been very little variation in the money supply over time.
B) there may be a time lag between a change in the money supply and its effects on nominal GDP.
C) there is only one definition of the money supply.
D) it is difficult to measure the value of nominal GDP over time.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 18.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 18.3
-Refer to Figure 18.3.A cut in tax rates will decrease tax revenue if the economy moves from Point
Figure 18.3
-Refer to Figure 18.3.A cut in tax rates will decrease tax revenue if the economy moves from Point
A) A to B.
B) B to A.
C) C to B.
D) A to D.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Lucas supply function,in combination with the assumption that expectations are rational,implies that an announced monetary policy change will
A) not change output.
B) decrease output,but never increase output.
C) either increase or decrease output,depending on the type of monetary policy change.
D) increase output,but never decrease output.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to supply-side economics,the government needs to focus on policies to
A) stimulate demand.
B) decrease demand.
C) stimulate supply.
D) decrease supply.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to monetarists
A) the economy is relatively stable.
B) economic policy is effective in increasing output.
C) the economy is very unstable.
D) government spending is the main source of inflation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most empirical data support the idea that money demand depends on the interest rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Keynesians believe the economy can be managed using monetary and fiscal policy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Lucas supply function,workers who experience a positive price surprise will work fewer hours when
A) there is no substitution effect from a positive price surprise.
B) there is no income effect from a positive price surprise.
C) the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
D) the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to supply-side economists,as tax rates are reduced,labor supply should increase.This implies that
A) the income effect of a wage change is greater than the substitution effect of a wage change.
B) the substitution effect of a wage change is greater than the income effect of a wage change.
C) there is no income effect when tax rates are changed.
D) there is no substitution effect when tax rates are changed.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If nominal GDP is $200 billion and the stock of money is $40 billion,the velocity is 5.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Lucas supply function,if people's expectations are on target,then the amount of output they produce
A) is not related to the price level.
B) is directly related to the price level.
C) will always be below potential GDP.
D) will always be above potential GDP.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is difficult to empirically test alternative macroeconomic models against one another because
A) macroeconomic models do not predict the same outcomes from policies.
B) macroeconomic models differ in ways that are hard to standardize for.
C) macroeconomic models cannot be expressed in mathematical terms.
D) macroeconomic models are always expressed in scientific terms.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 147
Related Exams