A) increase and real domestic output will increase.
B) decrease and real domestic output will increase.
C) increase and real domestic output will decrease.
D) decrease and real domestic output will decrease.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A fall in real interest rates will reduce aggregate demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
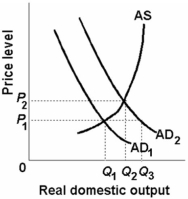 -Refer to the above diagram. If equilibrium real output is Q2, then:
-Refer to the above diagram. If equilibrium real output is Q2, then:
A) aggregate demand is AD1.
B) the equilibrium price level is P1.
C) producers will supply output level Q1.
D) the equilibrium price level is P2.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price level decreases:
A) the demand for money falls and the interest rate falls.
B) holders of financial assets with fixed money values decrease their spending.
C) holders of financial assets with fixed money values have less purchasing power.
D) there is a decrease in consumer spending that is sensitive to changes in interest rates.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following table is for a particular country in which C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports. All figures are in billions of dollars.
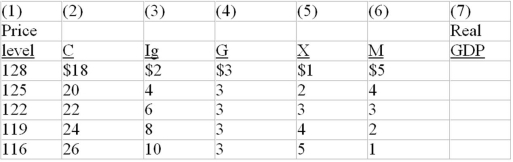 -Refer to the above table. The interest rate effect of changes in the price level is shown by columns:
-Refer to the above table. The interest rate effect of changes in the price level is shown by columns:
A) (1) and (4) of the table.
B) (5) and (6) of the table.
C) (1) and (3) of the table.
D) (2) and (4) of the table.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following would increase per unit production cost and therefore shift the aggregate supply curve to the left?
A) a reduction in business taxes
B) an increase in the number of resources used in production
C) an increase in the price of imported resources
D) deregulation of industry
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The real-balances effect indicates that:
A) an increase in the price level will increase the demand for money, increase interest rates, and reduce consumption and investment spending.
B) a lower price level will decrease the real value of many financial assets and therefore reduce spending.
C) a higher price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore increase spending.
D) a higher price level will decrease the real value of many financial assets and therefore reduce spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping because:
A) of the interest-rate effect.
B) higher price levels create incentives to expand output when resource prices remain constant.
C) of the net export effect.
D) higher price levels create an expectation among producers of still higher price levels.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the price level, other things equal, will shift the:
A) consumption, investment, and net exports schedules of the aggregate expenditures model downward.
B) consumption, investment, and net exports schedules of the aggregate expenditures model upward.
C) consumption, and investment schedules of the aggregate expenditures model upward, but the net exports schedule downward.
D) consumption, and net exports schedules of the aggregate expenditures model upward, but the investment schedule downward.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wage contracts, efficiency wages, and the minimum wage are explanations for why:
A) competition results in price wars.
B) wages tend to be inflexible downward.
C) the aggregate demand curve slopes downward.
D) there is little support for the existence of a real-balances effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram below. Suppose that aggregate demand increased from AD1 to AD2. For the price level to stay constant: 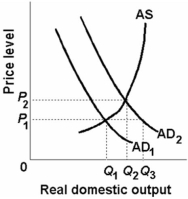
A) the aggregate supply curve would have to shift rightward.
B) the aggregate supply curve would have to shift leftward.
C) real domestic output would have to remain constant.
D) the aggregate supply curve would have to be vertical.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In deriving the aggregate demand curve from the aggregate expenditures model we note that:
A) the wealth or real balances effect is irrelevant to both models.
B) a change in the price level will have no impact on the aggregate expenditures schedule.
C) an increase (decrease) in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule upward (downward) .
D) an increase (decrease) in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule downward (upward) .
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A movement upward along an existing aggregate demand curve that changes the price level is equivalent to a(n) :
A) decrease in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate demand.
C) upward shift in the aggregate expenditures schedule.
D) downward shift in the aggregate expenditures schedule.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of aggregate supply, in the immediate short run:
A) the price level is variable.
B) real output is fixed.
C) nominal wages are variable.
D) both input prices and output prices are fixed.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Collective bargaining agreements that prohibit wage cuts for the duration of the contract contribute to:
A) a wealth effect.
B) a multiplier effect.
C) an increase in aggregate supply.
D) a price level that is inflexible downward.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the above information. All else being equal, if the price of each input increased from $4 to $6, productivity would:
A) fall from 2 to 3.
B) fall from .50 to .33.
C) rise from 1 to 2.
D) remain unchanged.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in aggregate supply would be caused by a change in:
A) the price level.
B) aggregate demand.
C) an aggregate supply determinant.
D) the quantity of real output supplied.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The foreign trade effect:
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B) shifts the aggregate demand curve leftward.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve rightward.
D) does none of the above.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An expected decline in the prices of consumer goods will:
A) decrease aggregate demand.
B) increase the quantity of real domestic output demanded.
C) increase aggregate demand.
D) decrease the quantity of real domestic output demanded.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long run aggregate supply:
A) is downward sloping.
B) is vertical.
C) is horizontal.
D) is upward sloping.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 195
Related Exams