A) any evolution at any scale
B) large-scale changes over a long period of time
C) small-scale changes over a long period of time
D) small-scale changes over a short period of time
E) changes of any scale within microorganisms Microevolution is the term applied to small changes in a population over relatively short periods of time.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Hardy-Weinberg formula, what does q2 represent?
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of the recessive allele
C) frequency of the heterozygotes
D) frequency of the homozygous dominants
E) frequency of the homozygous recessives
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If p = 0.6, what is q?
A) 0.6
B) 0.4
C) 0.36
D) 0.15
E) 0 Knowing the frequency of one allele, use the formula p + q = 1 to determine the frequency of the other allele.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The increase in frequency of dark phenotypes in response to increased pollution is called
A) genetic drift.
B) founder effect.
C) industrial melanism.
D) assortative mating.
E) stabilizing selection. The increase in frequency of dark phenotypes in response to increased pollution is called industrial melanism. The pollution generated by industry causes the trees to become blackened, which allows dark-colored individuals to blend in with the trees better than light-colored individuals.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
British land snails primarily occur in two extreme phenotypes. This is an example of
A) directional selection.
B) stabilizing selection.
C) disruptive selection.
D) genetic drift.
E) mutation. Disruptive selection favors polymorphism, the predominance of two or more phenotypes over an average phenotype.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of bacteria is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Through repeated exposure to an antibiotic, the frequency of the recessive allele is rapidly increasing. What is the most likely explanation for this response?
A) The recessive allele is responsible for susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotic.
B) The dominant allele is responsible for susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotic.
C) The recessive allele is responsible for resistance of the bacteria to the antibiotic.
D) The population is experiencing gene flow.
E) The population is experiencing disruptive selection. The frequency increase in one allele shows a violation of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Since the recessive allele is increasing in response to antibiotic exposure a selective agent) , this allele must be responsible for an adaptive phenotype, most likely antibiotic resistance.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Directional selection in the modern horse is demonstrated by
A) the gradual decrease in size over time.
B) the rapid decrease in size over time.
C) the gradual increase in size over time.
D) the rapid increase in size over time.
E) the extinction of other horse species. Over time, horses gradually increased in overall size as an adaptation to their environment changing from forest to grassland. A directional change such as this indicates directional selection.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which Hardy-Weinberg condition is violated by sexual selection?
A) no mutations
B) no natural selection
C) random mating
D) no genetic drift
E) no gene flow The Hardy-Weinberg equation for equilibrium assumes that mutations, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and nonrandom mating do not occur.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely an example of a founder effect event?
A) A random small group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
B) A random large group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
C) A selected small group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
D) A random small group of a bird population migrates to an island and does not return to breed.
E) A random large group of a bird population migrates to an island and does not return to breed. An example of the founder effect would likely be a small random portion of a population, representing a fraction of the entire gene pool, moving to a new location. These individuals take with them few chance alleles, which will occur at a higher frequency than in the original population.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not generate genetic variation within a population?
A) genetic recombination
B) independent assortment of alleles
C) sexual reproduction
D) mutation
E) adaptation Genetic variation is required for evolution to occur. Genetic variation is generated through mutation, sexual reproduction, independent assortment of alleles, and genetic recombination.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fraction of the original green frog population survives to reproduce and generate a new population. If the survivors of the original population survived by chance, then this event is an example of
A) natural selection.
B) genetic drift.
C) founder effect.
D) industrial melanism.
E) gene flow. Chance survival is considered genetic drift.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Natural selection can favor directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection in the same population simultaneously.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If half of a population is homozygous recessive, what is p?
A) 0.5
B) 0.707
C) 0.25
D) 0.293
E) 0.1 The homozygous recessive genotype = q2. So, if q2 = 0.5, then q = 0.707. p + q = 1, and therefore p = 0.293.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of field mice crosses a highway and joins a new population of field mice on the other side, producing offspring with this population. This is an example of
A) gene flow.
B) genetic drift.
C) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
D) assortative mating.
E) hybridization. Gene flow, also called gene migration, is the movement of alleles among populations by migration of breeding individuals.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shown here represents stabilizing selection. What happens when an individual is produced that possesses a trait far away from the mean value? 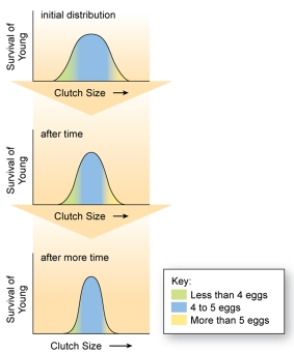
A) That extreme individual likely will not survive and reproduce.
B) That extreme individual will be more likely to survive and reproduce.
C) That extreme individual will have neither an advantage nor a disadvantage over other individuals.
D) All phenotypes have equal likelihood of surviving and reproducing.
E) The average phenotype is less likely to survive and reproduce. Stabilizing selection selects against individuals that are far from the mean value of a given trait.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what type of environment is being heterozygous in regards to the sickle-cell trait an advantage?
A) an environment that has malaria
B) an environment that is malaria-free
C) an environment that is exposed to a large amount of sunlight year-round
D) an environment that is degraded
E) an environment that is cold and rainy Being heterozygous in an environment that has malaria is advantageous. The heterozygote produces red blood cells that secrete potassium, which causes the malaria parasite to die.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure shown here, petal color of a flower population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve. If the pink petal color increases in frequency in the population, this would illustrate
A) stabilizing selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift. Stabilizing selection selects against individuals that are far from the mean value of a given trait.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In random mating
A) individuals choose the most attractive mate.
B) there is no factor influencing mate choice.
C) breeding occurs between two different species.
D) breeding occurs between two different subspecies.
E) fertile offspring are not produced. Random mating is when there are no factors influencing mate choice.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The usage of the insecticide DDT to control mosquitoes resulted in
A) directional selection to insecticide resistance in the insects.
B) stabilizing selection to insecticide resistance in the insects.
C) disruptive selection to insecticide resistance in the insects.
D) genetic drift to insecticide resistance in the insects.
E) no change in the insect population. Directional selection occurred in mosquitoes over years of exposure to DDT. Those individual mosquitoes that were resistant to insecticide survived and reproduced. Subsequent generations of mosquitoes showed resistance to DDT.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following examples describes genetic drift?
A) A forest fire kills all plant life south of a highway.
B) Rabbits with longer fur survive the winter.
C) Insects resistant to insecticide survive crop dusting.
D) Colorful lizards living on brown leaves are most often eaten by predators.
E) Plants with larger flowers attract more butterflies than plants with smaller flowers. Genetic drift refers to random survival and reproduction, regardless of adaptive traits.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 44
Related Exams