A) 7 percent.
B) 3 percent.
C) −3 percent.
D) −7 percent.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed doubled the money supply in one day, the amount of goods and services traded would:
A) not change.
B) increase.
C) decrease.
D) collapse.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity equation states:
A) M ×V = P ×Y.
B) M ×P = Y ×V.
C) P ×V = M ×Y.
D) M ×Y = P ×V
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists agree that modest inflation is desirable over zero inflation because:
A) it helps firms to more easily adjust real wages.
B) it allows a margin of error for those deciding on the money supply.
C) it allows the Fed to more easily engage in expansionary monetary policy.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While the __________ is not important, the _________ can have a big effect on economic behavior.
A) price level; unpredicted change in the price level
B) unpredicted change in the price level; price level
C) price level; predictable change in the price level
D) predictable change in the price level; price level
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The NAIRU:
A) is difficult to measure.
B) can change over time.
C) occurs at the economy's level of potential output.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the nominal interest rate is 7 percent annually, and you deposit $1,000. Inflation in the economy throughout the year is 7 percent. At the end of the year, you have earned:
A) an increase in your purchasing power.
B) no increase in your purchasing power.
C) no increase in your savings.
D) a decrease in your purchasing power.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
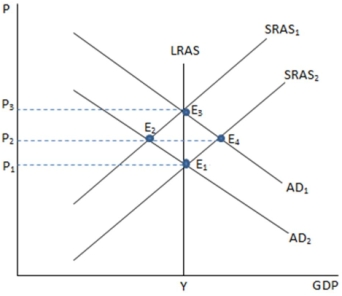 If the economy is represented in the graph shown and is currently at point E2, which action is the Fed most likely to undertake?
If the economy is represented in the graph shown and is currently at point E2, which action is the Fed most likely to undertake?
A) Expansionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the right.
B) Contractionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the left.
C) Expansionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the left.
D) Contractionary monetary policy, because it will shift AS to the right.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy has a money supply of $200, a velocity of 12, and a price level of $2, the output level must be:
A) 1,200 units.
B) 2,400 units.
C) 600 units.
D) 6,000 units.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed were to push unemployment below NAIRU, it is likely that:
A) inflation will increase.
B) deflation will send the economy into a deflationary spiral.
C) the dual mandate will be met.
D) the economy would be operating efficiently.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 1,000 units of output with a price level of $1 and the money supply (M) is $500, velocity is:
A) 2.
B) 500.
C) 50.
D) 5.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which measure of inflation best reflects changing prices for the average consumer?
A) Headline inflation
B) Core inflation
C) Hyper inflation
D) Nominal inflation
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The line that shows the connection between inflation and unemployment in the short run is called the:
A) Phillips Curve.
B) inflation-employment trade-off.
C) price-work curve.
D) aggregate supply.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Temporary changes in the price level caused by changes in the business cycle are called:
A) demand pull inflation.
B) cost push inflation.
C) demand push inflation.
D) cost pull inflation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to meet the dual mandate, the Fed must:
A) maintain price stability.
B) maintain full employment.
C) keep unemployment levels near the NAIRU.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An overall rise in prices in the economy is called:
A) inflation.
B) deflation.
C) core inflation.
D) core deflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The money, time, and opportunity used to change prices to keep pace with inflation are called:
A) menu costs.
B) shoe-leather costs.
C) tax distortions.
D) the velocity of inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If unemployment is below the NAIRU, inflation generally:
A) accelerates.
B) decelerates.
C) becomes negative.
D) gets caught in a downward spiral.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 3,000 units of output with a price level of $2 and with a velocity of money of 12, we know that the money supply must be:
A) $1,000.
B) $500.
C) $2,000.
D) $4,000.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate price level is:
A) a measure of the average price level for GDP.
B) measured by the CPI.
C) measured by the GDP price deflator.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 162
Related Exams