A) in favor of the gold standard and was given in 1896.
B) against the gold standard and was given in 1896.
C) in favor of the gold standard and was given in 2008.
D) against the gold standard and was given in 2008.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A measure of the average price level for GDP is called the:
A) aggregate price level.
B) national price level.
C) economy price level.
D) total price level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disinflation is the term for a period during which overall inflation rates are:
A) positive and falling.
B) negative.
C) positive and increasing.
D) zero.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The velocity of money is:
A) the number of transactions a typical dollar is used in during a given period.
B) the number of goods a typical dollar can buy in a given period.
C) how quickly money is created through the financial system.
D) how quickly money will be accepted as a medium of exchange in a given period.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
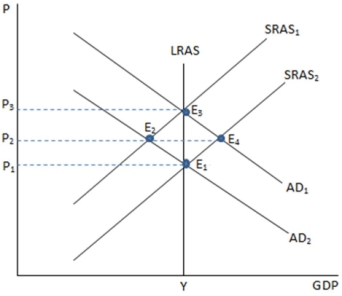 If the economy is in a recession, which point in the graph shown would likely represent this?
If the economy is in a recession, which point in the graph shown would likely represent this?
A) E1
B) E2
C) E3
D) E4
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ inflation is more stable than __________ inflation, because it ____________.
A) Core; headline; excludes food and gasoline prices
B) Headline; core; excludes food and gasoline prices
C) Core; headline; does not exclude food and gasoline prices
D) Headline; core; does not exclude food and gasoline prices
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy experiences deflation, investment will:
A) decrease, because businesses will not take out loans that will increase in value over time.
B) increase, because businesses will take out loans that will increase in value.
C) decrease, because businesses will spend cash instead of borrowing it.
D) increase, because businesses will spend cash instead of borrowing it.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The net result of deflation is to:
A) reduce the level of aggregate demand in the economy.
B) increase the level of aggregate demand in the economy.
C) be neutral and not affect the aggregate demand in the economy.
D) reduce the level of aggregate supply in the economy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 5,000 units of output with a price level of $1 and with a velocity of money of 4, we know that the money supply must be:
A) $4,000.
B) $1,250.
C) $2,500.
D) $5,000.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed were to allow unemployment to remain at a higher level than NAIRU:
A) It would lead to deflation.
B) the dual mandate would be violated.
C) they would fail to maintain full employment.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the costs not associated with predictable inflation is:
A) menu costs.
B) shoe-leather costs.
C) tax distortions.
D) labor costs.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the quantity theory of money, increasing the money supply:
A) leads to inflation.
B) causes production to increase.
C) leads to decreased spending.
D) causes each dollar to be spent less often.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Subtracting the inflation rate from the nominal rate of interest tells you the:
A) nominal rate of return.
B) real interest rate.
C) real rate of inflation.
D) price level of the economy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the prices of food and gasoline are added to core inflation, we get:
A) core deflation.
B) headline inflation.
C) hyperinflation.
D) adjusted inflation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed conducts expansionary monetary policy, it __________ in the short run, but __________ in the long run.
A) boosts demand; causes inflation
B) causes inflation; boosts output
C) causes inflation; boosts economic growth
D) boosts demand; boosts supply
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 1,000 units of output with a price level of $5 and the money supply (M) is $1,000, velocity is:
A) 5.
B) 200.
C) 50.
D) 2.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Menu costs refer to:
A) the money, time, and opportunity used to change prices to keep pace with inflation.
B) the time, money, and effort one has to spend managing cash in the face of inflation.
C) being penalized via taxes for making more money in dollars, even though real purchasing power hasn't changed.
D) labor costs associated with inflation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The constant velocity of money in the quantity equation implies that any increase in the money supply has to lead directly to:
A) an increase in P.
B) an increase in V.
C) an increase in Y.
D) a decrease in P.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the nominal interest rate is the same as the real interest rate, then inflation must be:
A) zero.
B) higher than the nominal rate of interest.
C) lower than the nominal rate of interest.
D) negative.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To measure core inflation, the BLS removes goods that:
A) have historically volatile prices.
B) are considered necessities.
C) are luxury goods.
D) are durable and hold a constant value.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 162
Related Exams