A) aggregate demand curve.
B) aggregate supply curve.
C) inflation rate.
D) business cycle.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between the price level and net exports is:
A) negative.
B) positive.
C) perfectly correlated.
D) uncorrelated.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The wealth effect explains the:
A) downward-sloping aggregate demand curve.
B) upward-sloping aggregate demand curve.
C) downward-sloping aggregate supply curve.
D) upward-sloping aggregate supply curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the period that many call the Great Recession:
A) GDP fell.
B) unemployment rose.
C) there was a sharp decrease in consumer spending.
D) All of these are true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in consumer confidence will cause a:
A) movement downward along the aggregate demand curve.
B) shift in aggregate demand to the right.
C) shift in aggregate demand to the left.
D) movement upward along the aggregate demand curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of a shift in the aggregate demand curve due to an increase in consumer confidence will be:
A) an increase in both prices and output in the short run.
B) a decrease in prices only in the long run; output will remain the same.
C) a decrease in both prices and output in the short run.
D) an increase in output only in the long run; prices will remain the same.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In macroeconomics, the long run is determined by:
A) how long it takes for prices of inputs to adjust through the whole economy.
B) how long it takes for firms to vary all input quantities.
C) the longest contract length of a business.
D) how long it takes for output decisions to adjust to changes in economic conditions.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the economy fluctuates around its long-run aggregate supply:
A) it is called the business cycle.
B) the economy is in a state of chaos.
C) the value of currency becomes unstable.
D) we must be in a recession.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would likely cause aggregate demand to shift to the left?
A) Higher interest rates discouraging borrowing
B) Higher tariffs on all imports into the United States
C) Greater consumer confidence about the future
D) All of these would likely cause aggregate demand to shift to the left.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run aggregate:
A) demand is fixed.
B) supply is fixed.
C) demand tends to shift to the right.
D) supply tends to shift to the left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) vertical.
D) upward sloping.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the long run would be: 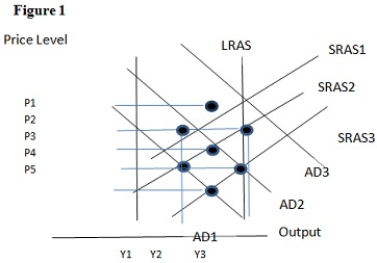
A) P1 and Y2.
B) P2 and Y2.
C) P1 and Y1.
D) P4 and Y2.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a change in the U.S. price level caused U.S. imports to increase, it must be true that the price level:
A) increased.
B) decreased.
C) became elastic.
D) became negative.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which three macroeconomic variables together best describe the health of the economy?
A) Output, GDP, and inflation
B) Output, inflation, and prices
C) GDP, unemployment, and employment
D) Output, prices, and employment
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, it is easier to:
A) adjust final prices rather than input prices.
B) adjust input prices rather than final prices.
C) change wage rates for employees than other input prices.
D) change input prices than output level.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An asset-price bubble is caused by:
A) people buying assets because they believed prices would keep going up and they'd be able to sell for a profit.
B) fads that make owning a certain asset fashionable.
C) severe inflation within a short period of time.
D) the increase in the value of durable goods when the economy is experiencing low inflation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the costs of production will cause the:
A) short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the right.
B) aggregate demand curve to shift to the right.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If U.S. prices increase relative to the rest of the world, we would expect imports:
A) to increase and exports to fall.
B) to decrease and exports to increase.
C) as well as exports to increase.
D) as well as exports to decrease.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is a negative relationship between the price level and which components of GDP?
A) C, I, and G
B) I, G, and NX
C) C, G, and NX
D) C, I, and NX
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long run result of the government responding to a negative supply side shock with increased spending will be a:
A) faster recovery, but it will cause even greater inflation.
B) slower recovery, if they misjudge their own spending.
C) faster recovery at a lower price level than allowing short-run aggregate supply to adjust on its own.
D) slower recovery, but it will cause inflation to be lower than if they did nothing.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 178
Related Exams